
Overview
John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the adoption of anesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the fathers of modern epidemiology, in part because of his work in tracing the source of a cholera outbreak in Soho, London, in 1854. His findings inspired fundamental changes in the water and waste systems of London, which led to similar changes in other cities, and a significant improvement in general public health around the world.
Early life and education
Snow was born on 15 March 1813 in York, England, the first of nine children born to William and Frances Snow in their North Street home, and was baptised at All Saints’ Church, North Street, York. His father was a labourer who worked at a local coal yard, by the Ouse, constantly replenished from the Yorkshire coalfield by barges, but later was a farmer in a small village to the north of York.
The neighbourhood was one of the poorest in the city, and was frequently in danger of flooding because of its proximity to the River Ouse. Growing up, Snow experienced unsanitary conditions and contamination in his hometown. Most of the streets were unsanitary and the river was contaminated by runoff water from market squares, cemeteries and sewage.
From a young age, Snow demonstrated an aptitude for mathematics. In 1827, when he was 14, he obtained a medical apprenticeship with William Hardcastle in Newcastle-upon-Tyne. In 1832, during his time as a surgeon-apothecary apprentice, he encountered a cholera epidemic for the first time in Killingworth, a coal-mining village. Snow treated many victims of the disease and gained a lot of experience. Additionally, while he was an apprentice, Snow could not drink, gamble or marry. Eventually he adjusted to teetotalism and led a life characterized by abstinence, signing an abstinence pledge in 1835. Snow was also a vegetarian and tried to only drink distilled water that was pure. Between 1833 and 1836 Snow worked as an assistant to a colliery surgeon, first in Burnopfield, County Durham, and then in Pateley Bridge, West Riding of Yorkshire. In October 1836 he enrolled at the Hunterian school of medicine on Great Windmill Street, London.
Career
In 1837, Snow began working at the Westminster Hospital. Admitted as a member of the Royal College of Surgeons of England on 2 May 1838, he graduated from the University of London in December 1844 and was admitted to the Royal College of Physicians in 1850. In 1850 he was also one of the founding members of the Epidemiological Society of London, formed in response to the cholera outbreak of 1849.
In 1857, Snow made an early and often overlooked contribution to epidemiology in a pamphlet, On the adulteration of bread as a cause of rickets.
Anaesthesia
John Snow was one of the first physicians to study and calculate dosages for the use of ether and chloroform as surgical anaesthetics, allowing patients to undergo surgical and obstetric procedures without the distress and pain they would otherwise experience. He designed the apparatus to safely administer ether to the patients and also designed a mask to administer chloroform. He personally administered chloroform to Queen Victoria when she gave birth to the last two of her nine children, Leopold in 1853 and Beatrice in 1857, leading to wider public acceptance of obstetric anaesthesia. Snow published an article on ether in 1847 entitled On the Inhalation of the Vapor of Ether. A longer version entitled On Chloroform and Other Anaesthetics and Their Action and Administration was published posthumously in 1858.
After finishing his medical studies in the University of London, he earned his MD in 1844. Snow set up his practice at 54 Frith Street in Soho as a surgeon and general practitioner. John Snow contributed to a wide range of medical concerns including anaesthesiology. He was a member of the Westminster Medical Society, an organisation dedicated to clinical and scientific demonstrations. Snow gained prestige and recognition all the while being able to experiment and pursue many of his scientific ideas. He was a speaker multiple times at the societys meetings and he also wrote and published articles. He was especially interested on patients with respiratory diseases and tested his hypothesis through animal studies. In 1841, he wrote, On Asphyxiation, and on the Resuscitation of Still-Born Children, which is an article that discusses his discoveries on the physiology of neonatal respiration, oxygen consumption and the effects of body temperature change. Therefore, his interest in anaesthesia and breathing was evident since 1841 and beginning in 1843, Snow experimented with ether to see its effects on respiration. Only a year after ether was introduced to Britain, in 1847, he published a short work titled, On the Inhalation of the Vapor of Ether, which served as a guide for its use. At the same time, he worked on various papers that reported his clinical experience with anaesthesia, noting reactions, procedures and experiments.
Though he thoroughly worked with ether as an anaesthetic, he never attempted to patent it; instead he continued to work and publish written works on his observations and research. Within two years after ether was introduced, Snow was the most accomplished anaesthetist in Britain. Londons principal surgeons suddenly wanted his assistance.
John Snow also studied chloroform, as much as he studied ether, which was introduced in 1847 by James Young Simpson, a Scottish obstetrician. He realised that chloroform was much more potent and required more attention and precision when administering it. Snow first realised this with Hannah Greener, a 15-year-old patient, who died on 28 January 1848 after a surgical procedure that required the cutting of her toenail. She was administered chloroform by covering her face with a cloth dipped in the substance. However, she quickly lost pulse and died. After investigating her death and a couple of deaths that followed, he realized that chloroform had to be administered carefully and published his findings in a letter to The Lancet.
Obstetric Anaesthesia
Snows work and findings were related to both anaesthesia and the practice of childbirth. His experience with obstetric patients was extensive and used different substances including ether, amylene and chloroform to treat his patients. However, chloroform was the easiest drug to administer. He treated 77 obstetric patients with chloroform. He would apply the chloroform at the second stage of labour and controlled the amount without completely putting the patients to sleep. Once the patient was delivering the baby they would only feel the first half of the contraction and be on the border of unconsciousness but not fully there. Regarding administration of the anaesthetic, Snow believed that it would be safer if another person that was not the surgeon applied it.
The use of chloroform as an anaesthetic for childbirth was seen as unethical by many physicians and even the Church of England. However, on 7 April 1853, Queen Victoria, asked John Snow to administer chloroform during the delivery of her eighth child. He then repeated the procedure for the delivery of her daughter, three years later. Medical and religious acceptance of obstetrical anaesthesia came after in the 19th century.
Cholera
Snow was a skeptic of the then-dominant miasma theory that stated that diseases such as cholera and bubonic plague were caused by pollution or a noxious form of “bad air”. The germ theory of disease had not yet been developed, so Snow did not understand the mechanism by which the disease was transmitted. His observation of the evidence led him to discount the theory of foul air. He first publicised his theory in an 1849 essay, On the Mode of Communication of Cholera, followed by a more detailed treatise in 1855 incorporating the results of his investigation of the role of the water supply in the Soho epidemic of 1854.
By talking to local residents (with the help of Reverend Henry Whitehead), he identified the source of the outbreak as the public water pump on Broad Street (now Broadwick Street). Although Snow’s chemical and microscope examination of a water sample from the Broad Street pump did not conclusively prove its danger, his studies of the pattern of the disease were convincing enough to persuade the local council to disable the well pump by removing its handle (force rod). This action has been commonly credited as ending the outbreak, but Snow observed that the epidemic may have already been in rapid decline:
There is no doubt that the mortality was much diminished, as I said before, by the flight of the population, which commenced soon after the outbreak; but the attacks had so far diminished before the use of the water was stopped, that it is impossible to decide whether the well still contained the cholera poison in an active state, or whether, from some cause, the water had become free from it.:51-52
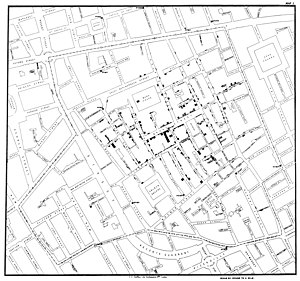
Original map by John Snow showing the clusters of cholera cases in the London epidemic of 1854, drawn and lithographed by Charles Cheffins.
Snow later used a dot map to illustrate the cluster of cholera cases around the pump. He also used statistics to illustrate the connection between the quality of the water source and cholera cases. He showed that the Southwark and Vauxhall Waterworks Company was taking water from sewage-polluted sections of the Thames and delivering the water to homes, leading to an increased incidence of cholera. Snow’s study was a major event in the history of public health and geography. It is regarded as the founding event of the science of epidemiology.
Snow wrote:
On proceeding to the spot, I found that nearly all the deaths had taken place within a short distance of the pump. There were only ten deaths in houses situated decidedly nearer to another street-pump. In five of these cases the families of the deceased persons informed me that they always sent to the pump in Broad Street, as they preferred the water to that of the pumps which were nearer. In three other cases, the deceased were children who went to school near the pump in Broad Street…
With regard to the deaths occurring in the locality belonging to the pump, there were 61 instances in which I was informed that the deceased persons used to drink the pump water from Broad Street, either constantly or occasionally…
The result of the inquiry, then, is, that there has been no particular outbreak or prevalence of cholera in this part of London except among the persons who were in the habit of drinking the water of the above-mentioned pump well.
I had an interview with the Board of Guardians of St James’s parish, on the evening of the 7th inst , and represented the above circumstances to them. In consequence of what I said, the handle of the pump was removed on the following day.
John Snow, letter to the editor of the Medical Times and Gazette

John Snow memorial and public house on Broadwick Street, Soho
Researchers later discovered that this public well had been dug only 3 feet (0.9 m) from an old cesspit, which had begun to leak faecal bacteria. The cloth nappy of a baby, who had contracted cholera from another source, had been washed into this cesspit. Its opening was originally under a nearby house, which had been rebuilt farther away after a fire. The city had widened the street and the cesspit was lost. It was common at the time to have a cesspit under most homes. Most families tried to have their raw sewage collected and dumped in the Thames to prevent their cesspit from filling faster than the sewage could decompose into the soil.
Thomas Shapter had conducted similar studies and used a point-based map for the study of cholera in Exeter, Seven years before John Snow, although this did not identify the water supply problem that was later held responsible.
Political controversy
After the cholera epidemic had subsided, government officials replaced the Broad Street pump handle. They had responded only to the urgent threat posed to the population, and afterward they rejected Snow’s theory. To accept his proposal would have meant indirectly accepting the fecal-oral route of disease transmission, which was too unpleasant for most of the public to contemplate.
It wasn’t until 1866 that William Farr, one of Snow’s chief opponents, realized the validity of his diagnosis when investigating another outbreak of cholera at Bromley by Bow and issued immediate orders that unboiled water was not to be drunk.
Farr denied Snow’s explanation of how exactly the contaminated water spread cholera, although he did accept that water had a role in the spread of the illness. In fact, some of Farr’s statistical data that he collected helped promote John Snow’s views.
Public health officials recognise the political struggles in which reformers have often become entangled. During the Annual Pumphandle Lecture in England, members of the John Snow Society remove and replace a pump handle to symbolise the continuing challenges for advances in public health.

